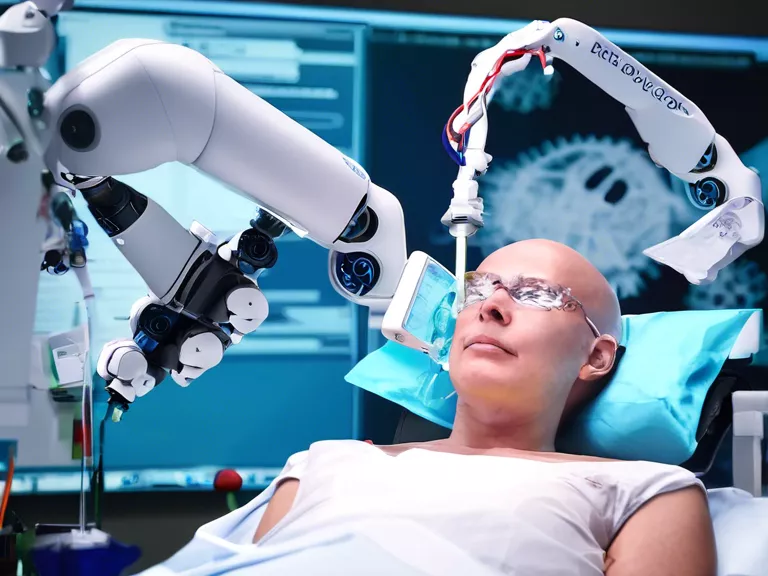
Robotics in surgery has transformed precision and accuracy in medical procedures. Robots are increasingly being used to assist surgeons in complex operations, leading to improved patient outcomes and shorter recovery times. In this article, we will explore the role of robotics in improving precision surgery techniques.
One of the key advantages of using robotics in surgery is the enhanced precision they provide. Robots can perform intricate tasks with greater accuracy than human hands, reducing the risk of human error. This precision is especially crucial in delicate procedures such as neurosurgery or microsurgery, where even the smallest mistake can have serious consequences.
Additionally, robotics allow surgeons to operate with greater control and stability. Robotic arms can be programmed to move with steady hands, eliminating the effects of hand tremors or fatigue. This ensures that surgeons can perform procedures with consistent precision throughout the operation.
Another benefit of robotics in surgery is the ability to access hard-to-reach areas of the body. Miniature robotic instruments can be inserted through small incisions, allowing surgeons to navigate tight spaces with ease. This minimally invasive approach reduces the risk of complications and speeds up the healing process for patients.
Furthermore, robotics enable surgeons to visualize the surgical site in greater detail. 3D imaging technology provides a clear, magnified view of the area being operated on, helping surgeons make more informed decisions during the procedure. This enhanced visualization leads to more accurate surgery and better patient outcomes.
Overall, the role of robotics in improving precision surgery techniques cannot be understated. From enhancing precision and control to enabling minimally invasive approaches and providing advanced visualization, robots are revolutionizing the field of surgery. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect robotics to play an even greater role in advancing surgical techniques and ultimately improving patient care.